Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 20 years old man, involved in MVA (motorbike versus car)
- On arrival to ED, BP=150/54mmHg, PR=105 bpm and GCS=10/15
- CBD gross hematuria.
- CT scan brain shows right extradural hemorrhage at temporal region with fracture at greater wing of right sphenoid (images not shown)
- Drop of hemoglobin during admission; Hb: 14 to 11.3 g.dL
- Blocked CBD, unable to pass urine and unable to reinsert new CBD.
- SPC done under ultrasound guidance
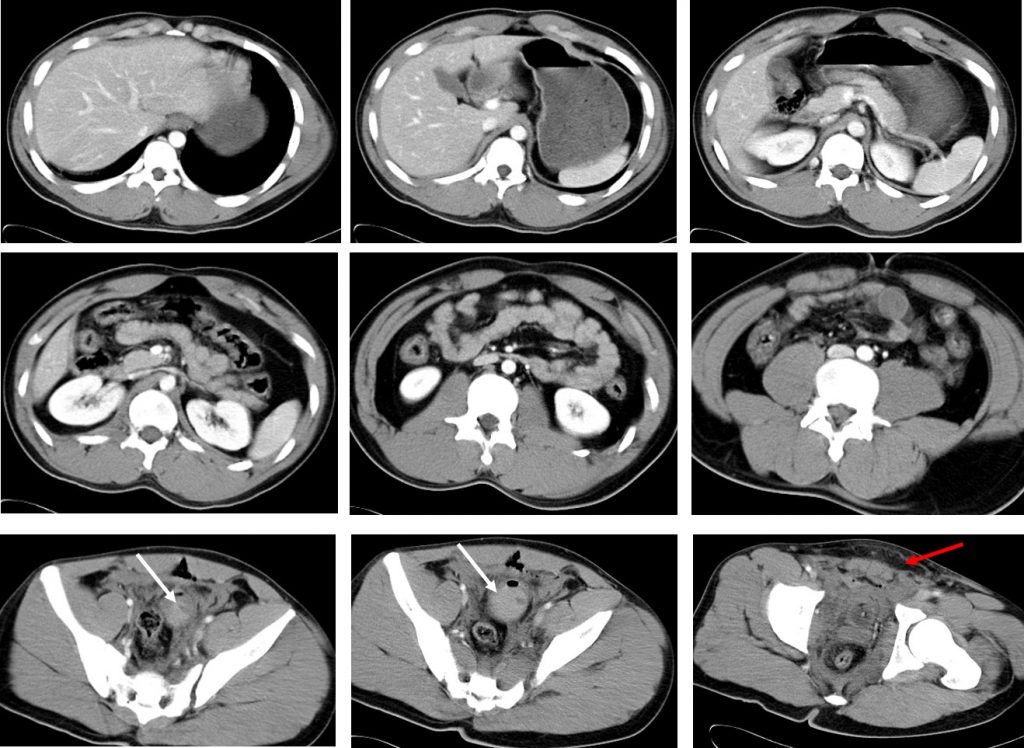
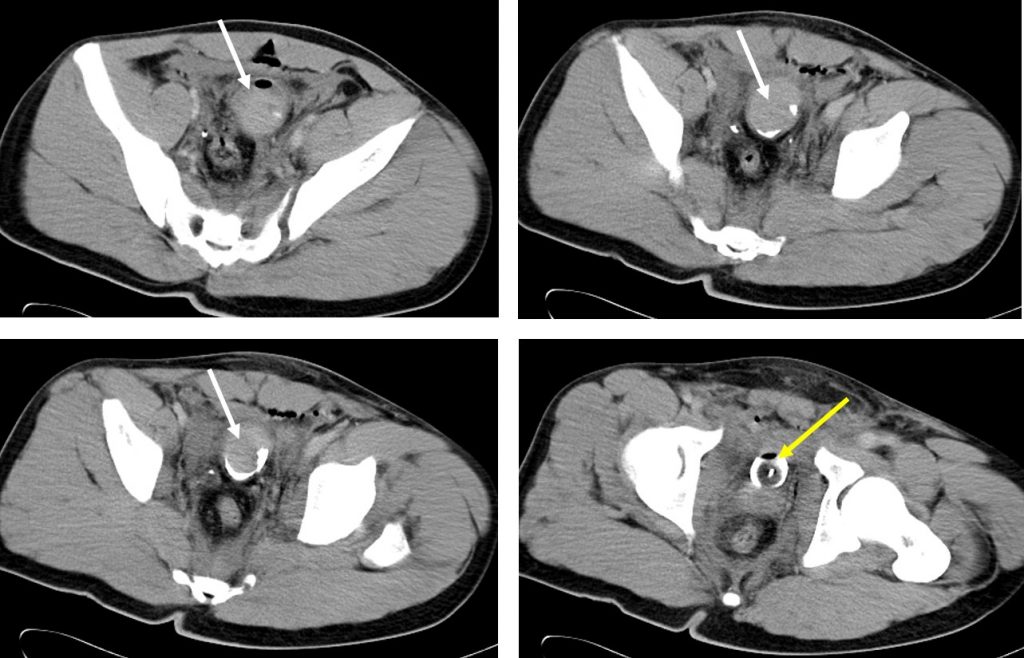
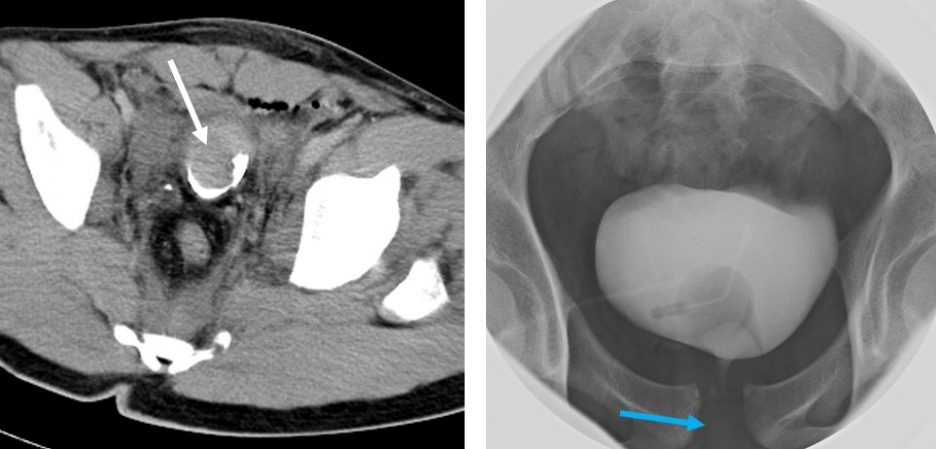
CT scan findings:
- No organ injury seen. No hemoperitoneum
- Blood clots are seen in the urinary bladder (white arrows)
- Air and CBD balloon within the bladder (yellow arrow)
- Soft tissue streakiness at perineum (red arrows)
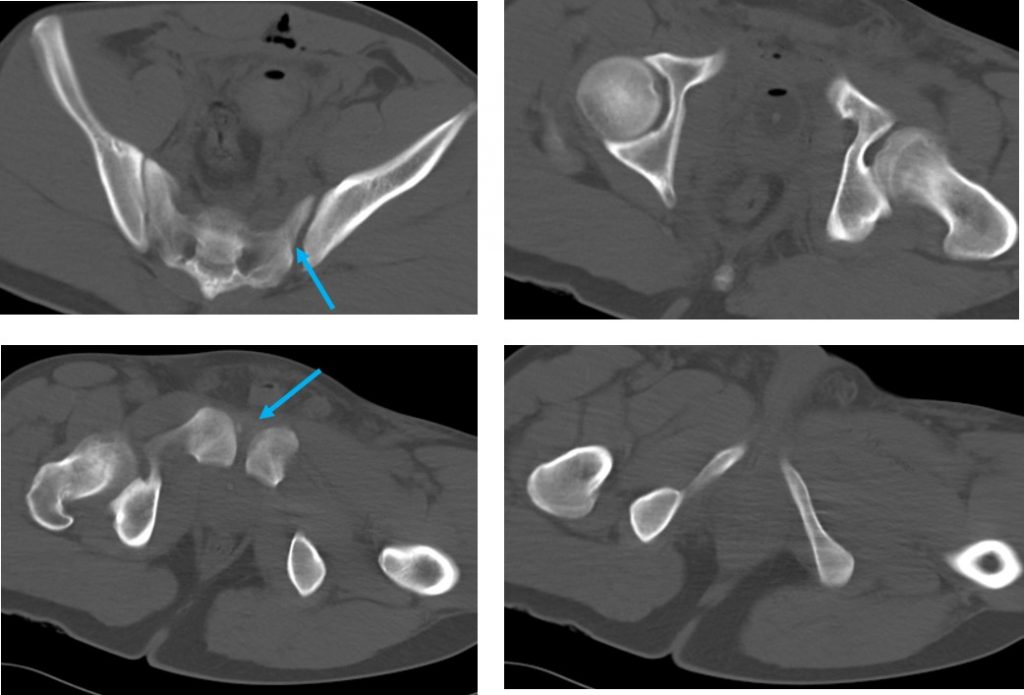
- Diasthesis of left sacroiliac joint and symphysis pubis (blue arrow)
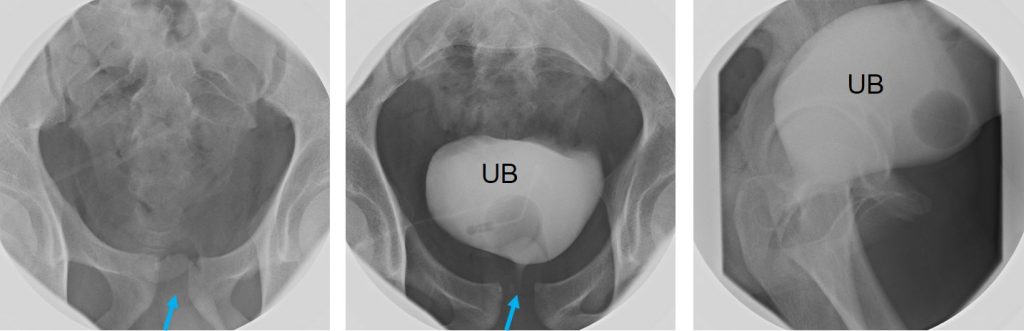
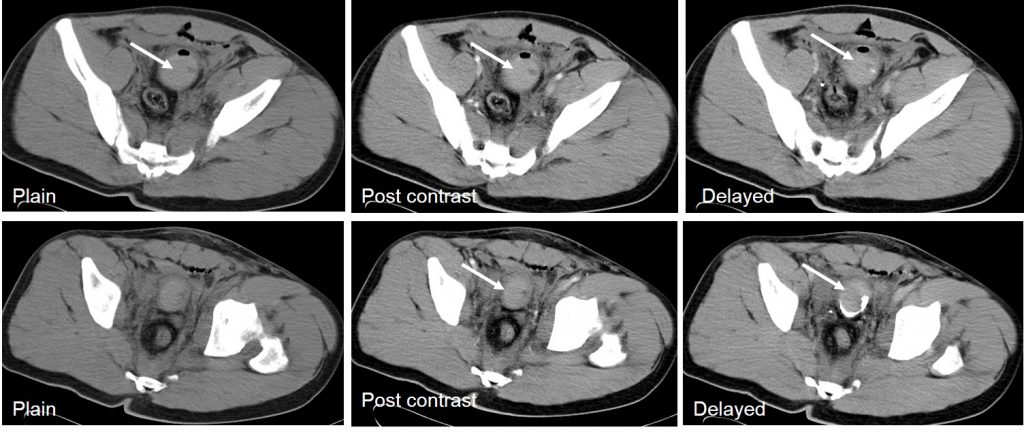
Flouroscopy examination:
- Symphysis pubis diasthesis as noted on previous CT scan (blue arrow)
- Contrast infused via SPC
- Urinary bladder is well distended, normal outline
- No extravasation of contrast seen
- Patient unable to pass urine
- Ascending urethrogram was planned but abandoned due to failure to cannulate the urethra
Cystoscopy examination done in OT
- Membranous urethral stricture almost 70% circumferentially
- SPC out of urinary bladder with encrusted tip of the catheter.
- SPC removal and urethral dilatation done
Diagnosis: Posterior urethral injury
Discussion:
- Injuries to the posterior urethra are most often related to motor vehicle accident and pelvic fractures (72%). Injury to the posterior urethra exclusively occurs in pelvic fractures with disruption of the pelvic ring.
- During deceleration impact injury, the severe shearing forces needed to fracture the pelvis are transmitted to the attachment of the perineal membrane and puboprostatic ligaments
- The highest risk of urethral injury is in straddle fractures with a concomitant diastasis of the sacroiliac joint. Displaced fractures of the inferomedial pubic bone and pubic symphysis diastasis, together with their degree of displacement, are independent predictors of urethral injury.
- Most posterior injuries occur at the bulbomembranous junction, distal to the external urethral spinchter.
- Posterior urethral injuries can result in significant delayed morbidity. Strictures, incontinence and erectile dysfunction (ED) are well-recognized associated problems that interfere with the quality of life.
Recent Comments