Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 55 years old lady
- No known medical illness
- Presented with epistaxis nasal stuffiness
- Clinical examination shows mass lesion in the nose
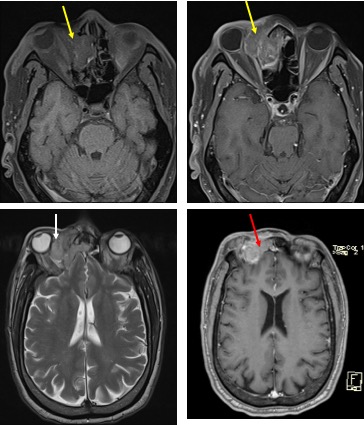
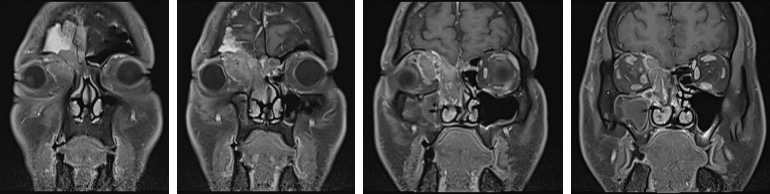
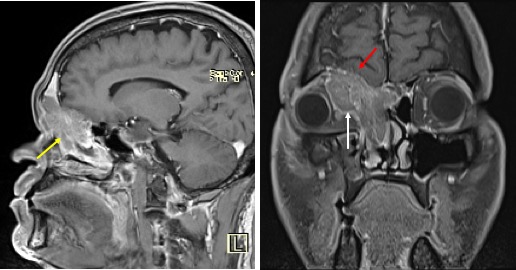
MRI findings:
- A large lobulated mass in the right ethmoidal sinus (yellow arrows)
- Extension into the right orbit (white arrow) causing distortion and displacement of the right globe
- Extension into the right maxillary sinus and inferior turbinate
- Intracranial extension indenting the frontal lobe gyrus (red arrow)
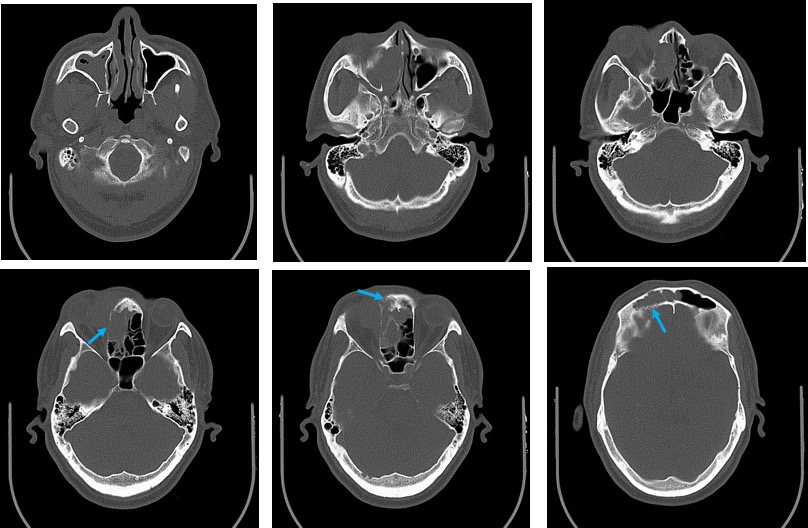
CT scan findings:
- Right proptosis
- Bone erosions are seen involving the right lamina papyracea
- Right nasal bone and wall of the frontal sinus are also involved
Diagnosis: Olfactory neuroblastoma (Esthesioneuroblastoma)-Biopsy proven
Discussion:
- Olfactory neuroblastoma also known as esthesioneuroblastoma
- It is tumour arising from basal layer of the olfactory epithelium in the superior recess of nasal cavity.
- Bimodal age distribution; 2nd decade and 5-6th decades
- No gender predilection
- The tumours are slow growing and begin as masses at superior olfactory recess and initially inolve the anterior and middle ethmoid air cells.
- As it grow, it can destroy surrounding bone and can extend in any direction. It can form ‘dumbbell-shaped’ with waist as it passes through the cribriform plate. Superior invasion to anterior cranial fossal, laterally to orbits and across the midline to the contralateral nasal cavity.
- Presence of cervical and retropharyngeal nodal metastasis is seen in 10-44% of cases at diagnosis.
- CT scan is good in assessment of extension and bone destruction. Focal calcificaitons are occasionally present. Bony margin remodelling and resorbed are seen.
- Variable enhancement usually moderate to intense
Recent Comments