Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 30 years old lady
- Presented with right breast lump for 3 years
- Slow increase in size, not painful
- No family history of breast cancer
- Clinically a palpable lump felt in the right breast
- FNAC done told no malignant cell seen
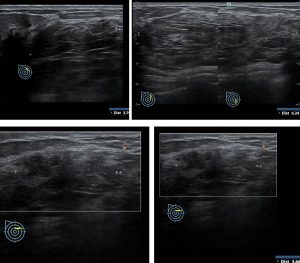
Ultrasound findings:
- There is a large lesion in the inner upper quadrant of right breast.
- This lesion is seen oval in shape with heterogenous echogenicity.
- The echogenicity is mainly following the normal breast tissue.
- There is no increase in vascularity and no penetrating vessels.
- The lesion is seen coursing along the plane of the breast tissue with no infiltration of the tissue anterior or posterior to it.
- No posterior shadowing.
- No dilated duct. No abnormal enlargement of axillary nodes.
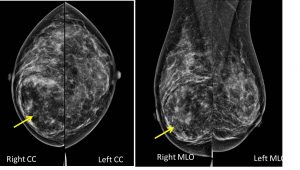
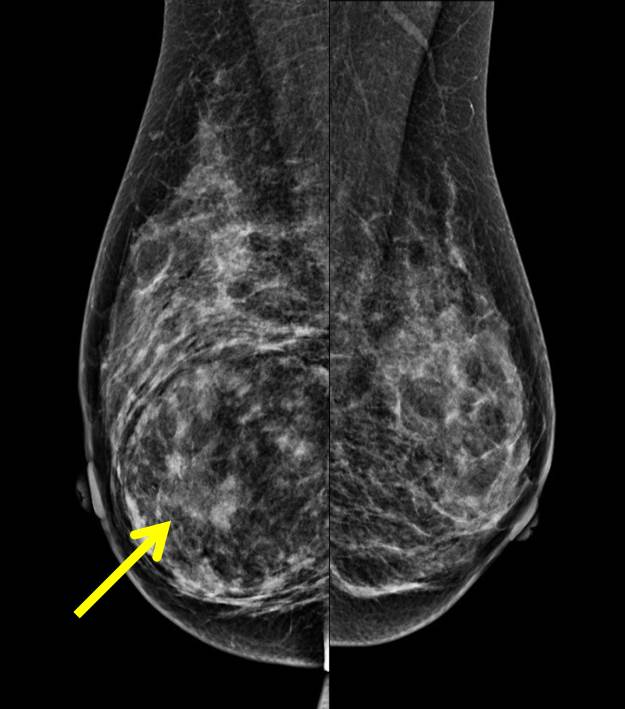
Mammographic findings:
- There is a well-defined lesion at right inner quadrant of right breast measuring about 8.0×6.0cm.
- The lesion is showed heterogenous density main similar to rest of breast tissue.
- There is compression and displacement of surrounding breast tissue seen with no obvious infiltration.
- There is no suspicious clutered microcalcification.
- There is no thickening of the overlying skin. No nipple retraction.
- No abnormal axillary nodes.
Diagnosis: Benign breast lesions; fibroadenolipoma
Discussion:
- Breast fibroadenolipomas are rare benign tumours.
- It is also known as breast hamartomas.
- It present as a soft, mobile, nodular lesion characterized by slow growth and vary in size from tiny masses to tumor-like formations measuring 10–12 cm in diameter, which may occupy almost the entire breast.
- It represent 4–8 % of the benign breast lesions diagnosed in women.
- They are extremely rare in males.
- Ultrasound in most cases appear as solid, well-defined, oval lesion lying parallel to the skin plane. The echo structure is inhomogeneous with hypoechoic areas intermixed with hyperechoic band-like or nodular areas, reflecting the presence of adipose, epithelial, and fibrous connective tissues.
- Hypervascularization is absent on color Doppler imaging.
- On mammogram these lesions are typically seen as oval or round formations, which are inhomogeneous with radio-opaque and radiotransparent areas reflecting the presence of tissues that differ in density.
- They are well defined by a thin radio-opaque pseudocapsule. The pseudocapsule is composed of breast parenchyma that has been displaced by the mass.
- The appearance has been described as ‘breast within a breast’ sign.
Recent Comments