Clinical:
- A 61 years old man with underlying DM, HPT and bronchial asthma
- Presented with sudden onset of double and blurred vision, right facial asymmetry and unsteady gait.
- On examination, there were right 3rd, 4th, 5th, 6th and 7th CN palsy with cerebellar signs.
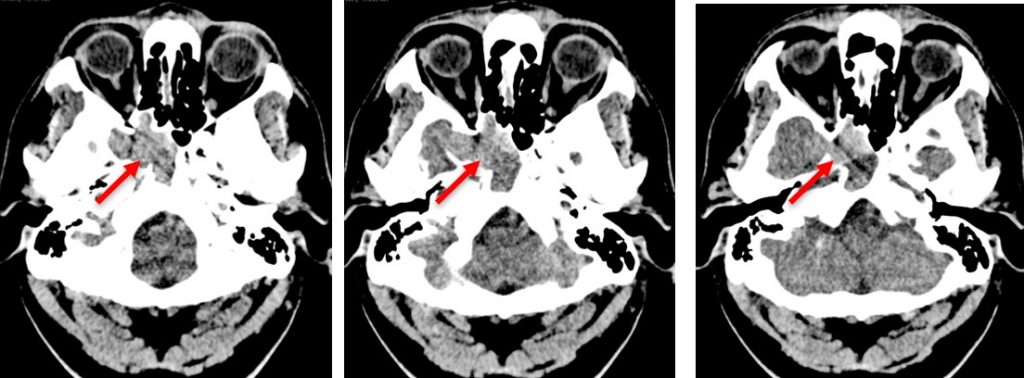
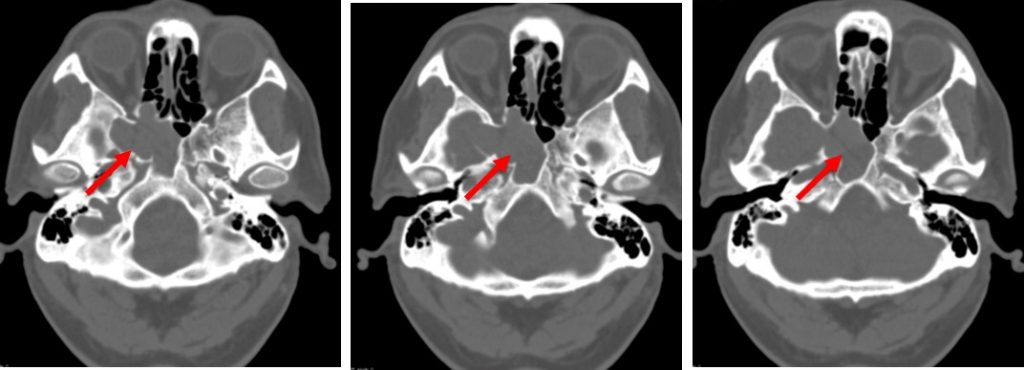
CT scan findings:
- Soft tissue density occupying right sphenoid sinus with evidence of sphenoid sinus expansion (red arrows)
- No focal brain parenchyma lesion. No intracranial bleed.
- No eye proptosis. No obvious extra-ocular muscles and optic nerve thickening.
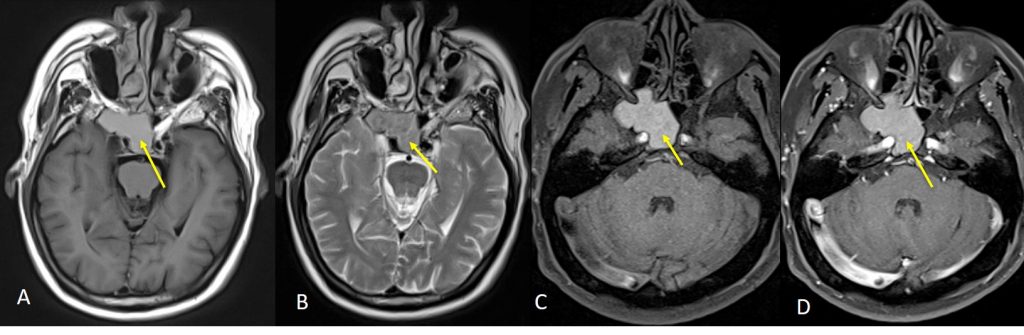
MRI findings:
- The right sphenoid sinus is expanded with homogenous material within the sinus cavity which is hyperintense on T1WI and isointense on T2WI (yellow arrows).
- There is no evidence of mucosal enhancement with gadolinium.
- The expanded sphenoid bone is obliterating the inferior portion of the right cavernous sinus causing a mild lateral convexity.
- Following contrast, enhancement of the cavernous sinuses are seen, with no clear demarcation seen between the enhances cavernous sinus and the expanded sphenoid extension. The subjacent cavernous right ICA medial to the filling defect is patent with normal flow void appearance.
Diagnosis: Sphenoid mucocele
Discussion:
- Paranasal sinus mucocele is complete opacification of one or more paranasal sinuses by mucus.
- It is often associated with bony expansion due to obstruction of the nasal sinus drainage.
- CT and MRI are best imaged with combination.
- Presence of air within affected sinus rules out the possibility of a mucocele.
- Xray shows opacification and expansion of affected sinus.
- CT shows affected sinus completely opacified, margins are expanded and usually thinned. Areas of bone resorption may be present causing bony defect and extension of ‘mass’ into soft tissue. Peripheral calcification sometimes seen. Minimal peripheral enhancement (if any) on post contrast.
- MRI shows signal intensity depends on proportion of water, mucus and protein content.
- Complications include:
- Subdural empyema, meningitis, cerebral abscess
- Subperiosteal abscess
- Subcutaneous infection
Recent Comments