Clinical:
- A 49 years old Malay lady
- Presented with abdominal discomfort for few years
- Sometimes pain related to menses
- Ultrasound examination by O&G team showed bilateral ovarian cyst
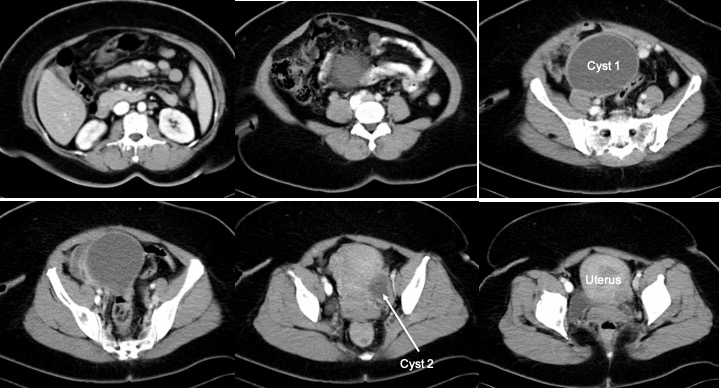
CT scan findings:
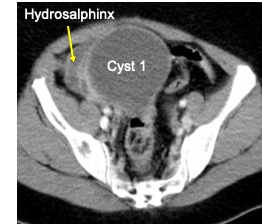
- A well-defined cystic lesion measuring 10x10x8 cm arising from the right adnexal region
- Another cyst measuring 4.0x 3.0 cm from the left adnexal region.
- No calcification or septa within the lesions
- No solid component
- No ascites. Other organ seems normal
Intraoperative findings:
- Right endometrioma 10×10 cm ruptured during manipulation. Distorted right fallopian tube with right hydrosalphix. Tube filled with chocolate endometriotic fluid. Adhesion of right fallopian tube to the bowels.
- Obliteration of Pouch Of Douglas.
- Endometriotic spots over the bowel.
- Adhesion and thickening of left ovary and tubes. Left hydrosalphinx filled with chocolate material.
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen consist of enlarged uterus and cervix, ruptured right ovarian cyst and bilateral fallopian tube (FT). The uterus measures 125 mm form fundus to cervi, 65 mm from cornu to cornu, 55 mm in AP diameter. Serial cut section of uterus show empty uterine cavity. The anterior and posterior endomyometrium measured 25-30 mm. The ruptured right ovarian cyst measures 90x80x25 mm. The wall is thick measuring 1-10 mm in thickness. There is brownish material stained the inner surface. The right FT is dilated measuring 75 mm in length and 25 mm in greatest dimension. The left FT measures 55 mm in length and 15 mm in diameter.
- Microscopy: section show the cyst wall devoid of epithelial lining and replaced by aggregates of hemosiderin laden macrophages. Areas of hemorrhage and scattered hemosiden laden macrophages are noted in the cyst wall stroma and the wall of right FT. A foci of endometrial glands and stroma are seen within the myometrium. The left ovary shows follicular cyst.
- Impression: Right ovarian endometriotic cyst. Uterus adenomyosis.
Diagnosis: Ovarian endometriotic cyst
Discussion:
- Endometriosis is defined as the presence of endometrial tissue outside of the uterine cavity and has an estimated prevalence of 5%–10% of women per year.
- Endometritic cyst occur when ectopic endometrial tissue implants enlarge and repeatedly hemorrhage in response to hormonal stimulation, forming cystic lesions commonly on the ovaries.
- Endometriotic cysts also known as endometrioma or chocolate cyst
- The cysts are usually small 2-5cm, however can be up to 20 cm in size.
- The location of endometriotic cysts: ovaries, anterior and posterior cul-de-sac, posterior broad ligament, uterosacral ligament, uterus and colon.
- The appearances of endometriomas can be quite variable. The classical example is a unilocular cyst with acoustic enhancement with diffuse homogeneous ground-glass echoes as a result of the hemorrhagic debris. This appearance occurs in 50% of cases.
- MRI is very useful and signal characteristic depends on age of hemorrhage.
