Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 23 years old lady
- No known medical illness
- Presented with tingling and pulling sensation of the left side of the face for the last few months
- Associated with reduce hearing left side and tinnitus.
- Clinical examination shows left facial nerve palsy, House Brackmann Grade III.
- Audiometry: conductive hearing loss of left ear.
- Otoscopy left ear: Dull TM, distorted malleolus.
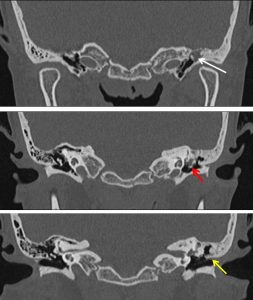
CT scan findings:
- Left external ear canal and tympanic membrane is intact.
- There is soft tissue density (mean HU 32) within the left middle ear cavity (white arrows), involving the mesotympanum, epitympanum and Prusak space.
- Hypotympanum is clear.
- Associated erosion to the tegmen tympani with blunted of scutum are noted (yellow arrow).
- The normal appearance of incudo-malleolar joint is not seen, suggestive of disruption (red arrows).
- Suspicious involvement of the tympanic segment of facial nerve is seen.
- The inner ear structures are normal in appearance and intact. No evidence of semicircular canal or facial nerve dehiscence.
- There is fluid density within the left mastoid air cells which associated with bone remodelling. The aditus ad antrum is otherwise clear.
Diagnosis: Cholesteatoma (HPE proven)
Discussion:
- Cholesteatoma is a well-demarcated non-neoplastic lesion in the temporal bone.
- The annual incidence of cholesteatoma is reported as 3-9 cases per 100 000 population.
- It is classified based on either the pathogenesis or the location in the middle ear cavity in relation to the tympanic membrane.
- HRCT is the imaging of choice due to its high sensitiviy. Typical findings include a sharply marginated expansile soft tissue lesion, retraction of the tympanic membrane, blunting of scutum and erosion of the tympanic tegmen and ossicles.
Progress of patient:
- Operation done in another hospital
- EUM with combined approach tympanoplasty and tympanoplasty type Vb
- Confirmed cholesteatoma
- Uneventful recovery
- Follow up assessment 2 months after surgery shows minimal left facial asymmetry, able to close eyes but not fully, minimal drooling of saliva when drinking.
