Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- An 83 years old man
- Known case of DM and hypertension on medication
- Presented with post prandial vomiting for one month
- Associated with loss of appetite and loss of weight (lost 20 kg in one month)
- No altered bowel habit
- Clinical examination is unremarkable
- OGDS: NO esophageal varices, pooling of bile in stomach about 1.2L sucked out, normal duodenum until second part, unable to go beyond second part as it coiled
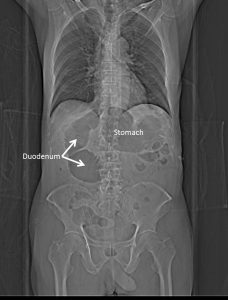
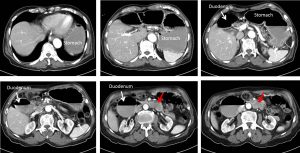
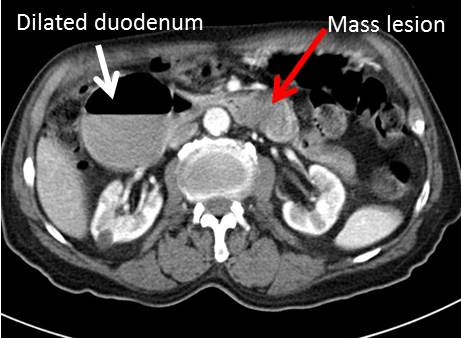
CT scan findings:
- The stomach and proximal (1st and 2nd) part of the duodenum is grossly dilated
- Air fluid levels are seen within this dilated part of bowel loops
- Soft tissue lesion is seen in distal part of duodenum (red arrows)
- No dilatation of bowel distal to this
- No abnormal enlargement of paraortic or paracaval node
- No ascites
Intra-operative findings:
- Exploratory laparotomy, duodenojejunostomy, jejunojejunostomy bypass and mesenteric nodule biopsy done
- Hard duodenal tumour near the duodenal jejunal junction, partly fixed with lesion over the neighbouring mesenteric/serosa of duodenum,
- The proximal duodenum is dilated,
- Multiple superficial liver nodule over the right lobe, peritoneal nodules over the visceral peritoneum distal to umbilicus
HPE findings: adenocarcinoma with metastasis to mesenteric nodes
Diagnosis: Duodenal adenocarcinoma
Discussion:
- Small bowel malignancies are relatively rare accounting for only 2% of all GIT cancers
- Among small bowel tumours, most malignancy arise from the ileum followed by duodenum and lastly the jejunum
- Duodenal adenocarcinoma is a rare but aggressive malignancy
- It comprises of less than 1% of all GIT cancers
- The causative factors have not been clearly identified
- Associated risk factors include duodenal adenomas and duodenal polyps
Progress of patient:
- Complicated post operatively by left psoas collection and sepsis
- Referred for palliative chemotherapy
- However chemotherapy as patient is not fit for further treatment
- On palliative care