Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 73 years old man
- Underlying hypertension on medication
- Presented with recurrent right facial pain
- Had been on several courses of antibiotic
- Clinical examination shows minimal swelling at right mandibular region which is non-tender on deep palpation. Good mouth opening.
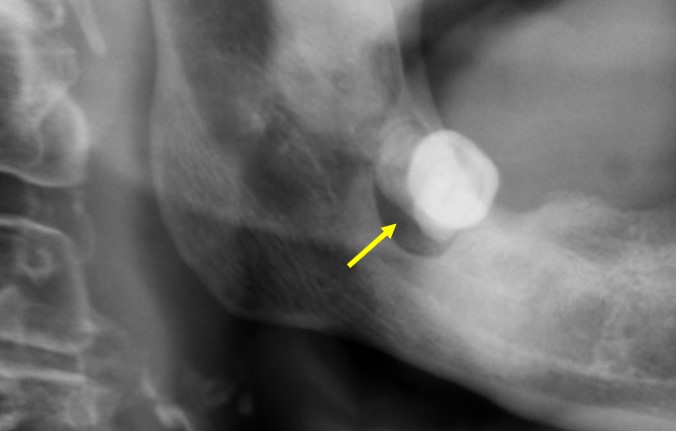
- Diagnosis of infected dentigerous cyst with impacted tooth 48
- Operation done: cyst enucleation and surgical removal of tooth 48 under GA
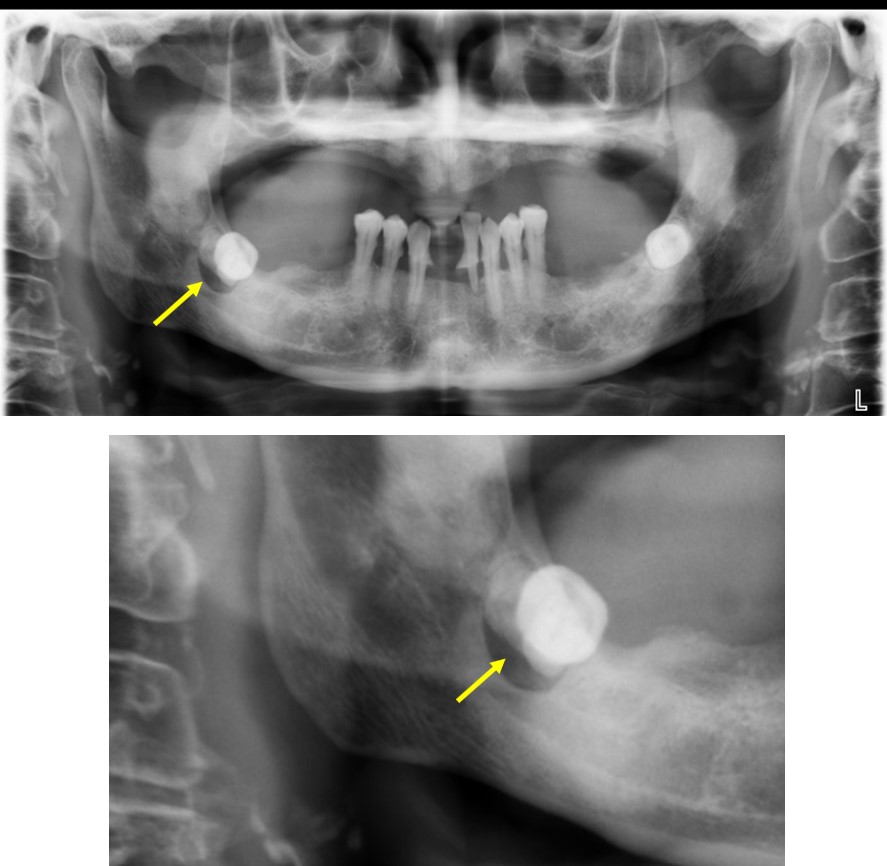
Orthopantomogram findings:
- A well-defined lucent area is seen at right mandible
- It is ovoid in shape with sclerotic border
- It is seen surrounding partially erupted root of third molar tooth
- There is no fluid level within the lesion
- No other lesion of visualized bones.
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as tissue surrounding root 48
- Microscopy: Sections show fibrous connective tissue of variable maturity lined in part by degenerated non-keratinising stratified squamous epithelium, which demonstrate arcading pattern in areas. There is a diffuse infiltration of mixed acute and chronic inflammatory cells. An area containing pool of haemorrhage also present. Trabeculae of woven and lamellar bones also observed.
- Interpretation: Consistent with dentigerous cyst and inflamed mucosa
Discussion:
- Dentigerous cyst is also known as follicular cyst
- It is the most common type of non-inflammatory odontogenic cyst and the most common cause of pericoronal lucency associated with impacted tooth.
- Most dentigerous cyst manifest in adolescent and young adult
- It is often found around the crown of an unerupted mandibular third molar tooth
- It can expand asymptomatically and potential to displace or resorb adjacent teeth or bone
- At radiography it appears as well-defined, round or ovoid lucent lesions around the crowns of unerupted teeth, usually third molar. Other location include maxillary third molar, maxillary canine and mandibular second premolar.
- The root of the involved tooth are often outside the lesion and located in mandibular bone.
- It can vary in size from 2 cm or larger and may cause mandibular expansion
- Treatment include extraction of associated tooth and removal of the entire cyst.