Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 13 years old girl
- Had underlying rhinosinusitis
- Presented with fever, headache and vomiting for one week
- Initially treated as AGE and sinusitis
- In ward noted to have left eye lateralization and limb weakness
MRI findings:
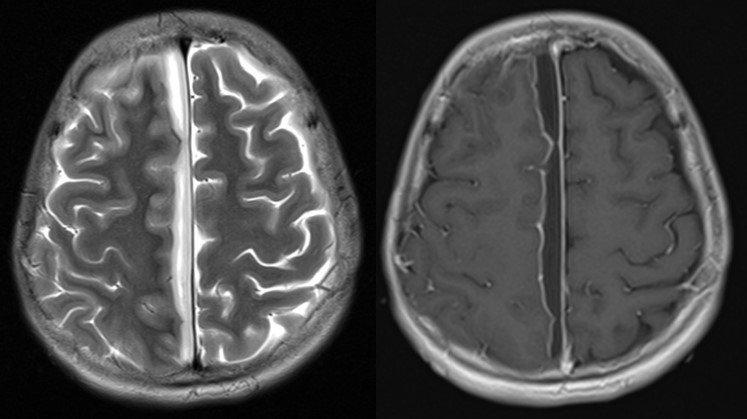
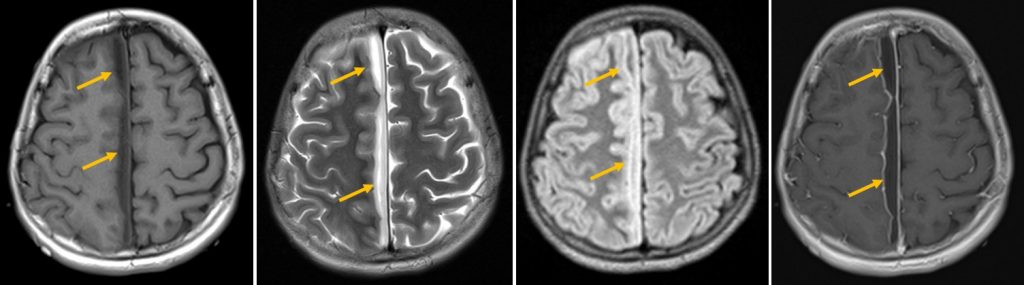
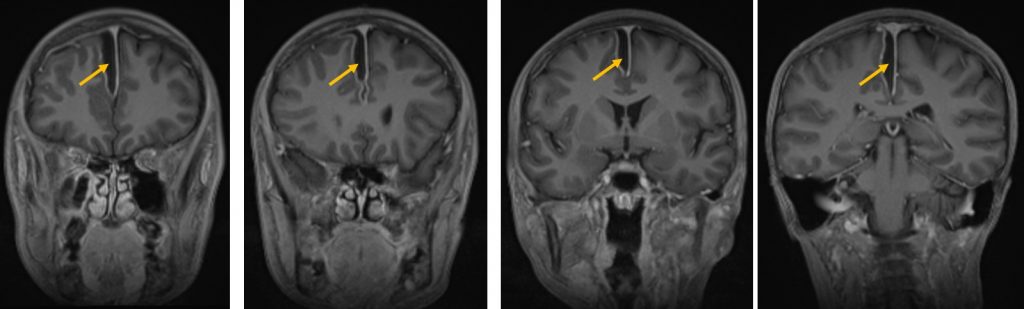
- A subdural right para-falcine collection
- Hypointense on T1, hyperintense on T2/FLAIR with peripheral enhancement post contrast.
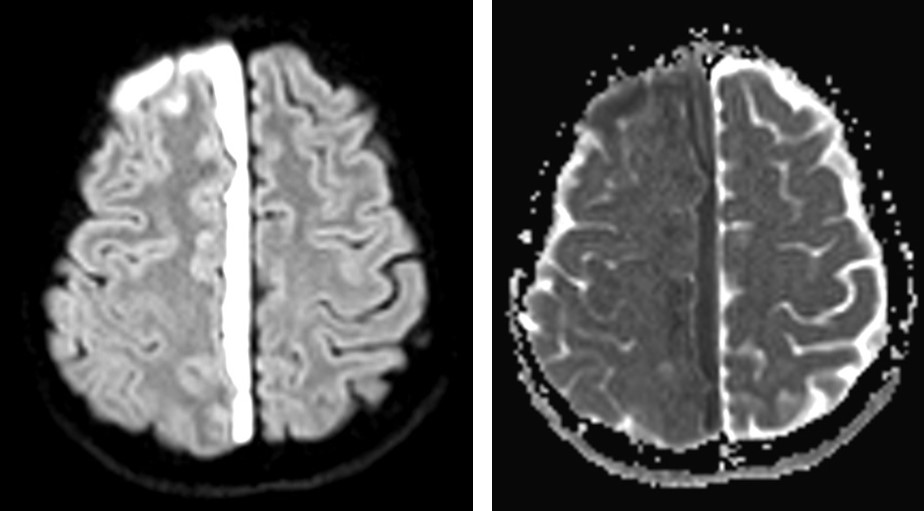
- It showed restricted diffusion on DWI/ADC sequences
- minimal mass effect is seen onto the adjacent cerebral parenchyma
- minimal effacement of the right cerebral hemisphere
- Cavernous and dural venous sinuses are normal.
Diagnosis: Parafalcine subdural empyema
Progress of patient:
- Burrhole drainage done, about 25-30 cc pus gushed out upon opening of dura.
- Pus culture no growth, pus cells 3+, epithelial cells 1+, no organism seen, AFB smear negative
- Responded well with antibiotics
Discussion:
- Subdural empyema is a collection of pus between the dura mater and underlying arachnoid mater.
- It is usually a complication of sinusitis or following an ear infection, cranial trauma or surgery and rarely bacteraemia.
- The most common causative organisms are streptococci.
- It may progress to meningitis, cortical vein thrombosis or brain abscess.
- On imaging it presents as crescentic collection with meningeal enhancement.
- CT shows similar appearance to subdural haematomas in their shape and relationship with dural reflections.
- MRI may show restricted diffusion.
- Mortality rate is reported about 10%.