Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 23 year old male with no known medical illness, presented with complaint of dizziness for 6 days, right eye dropping for 3 days and vomiting for 2 days.
- Otherwise, no fitting episode, no 1 side body weakness, no blurry of vision or double vision and no history of fall or trauma.
- CT Brain done noted pontine bleed involving left cerebral peduncle with mass effect and he was admitted for observation.
- Subsequently he was under clinic follow up.
- Upon our review in clinic, patient well, no sign and symptom of increase intracranial pressure.
- GCS E4V5M6, pupils 3/3 reactive. Vital signs are stable
- CNS: power 5/5 bilaterally with normotonia and normoreflexia
- Cranial nerve: no opthalmoplegia
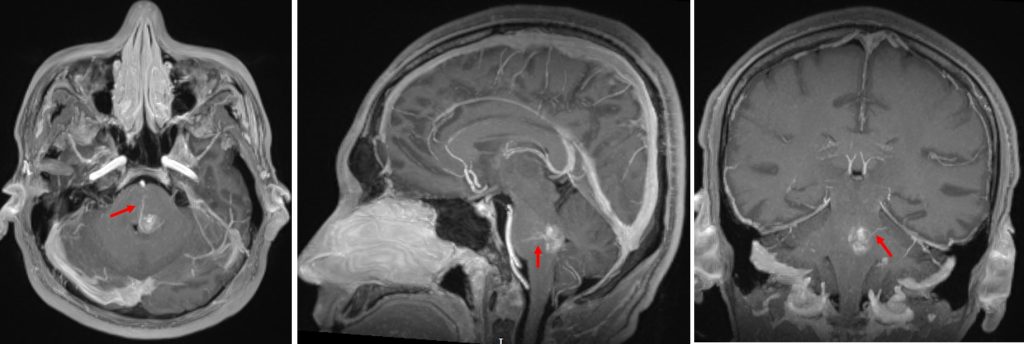
MRI findings:
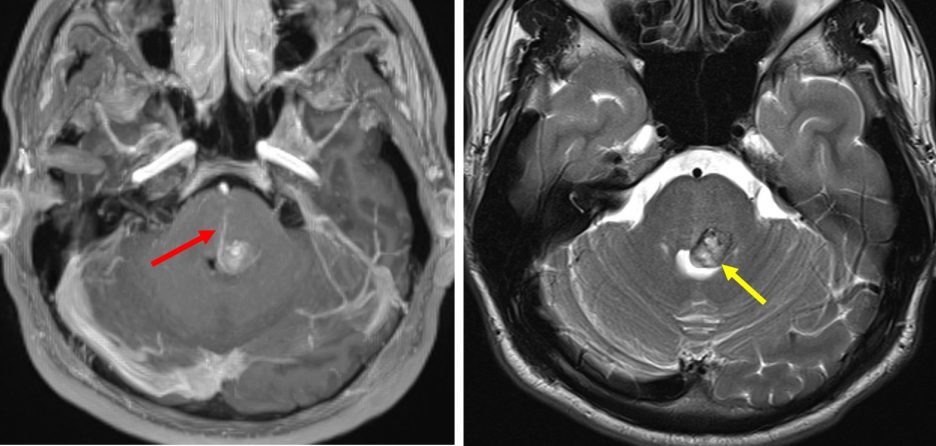
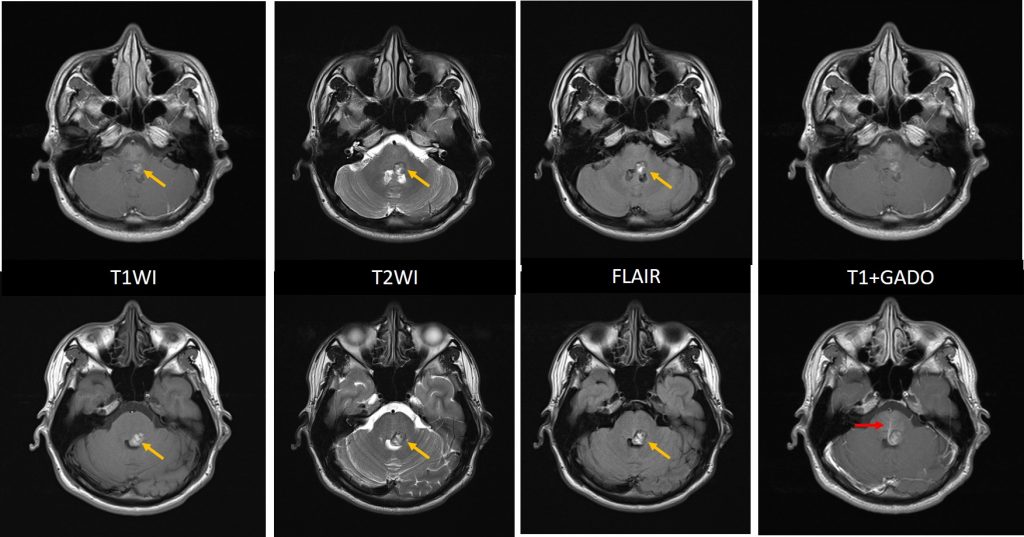
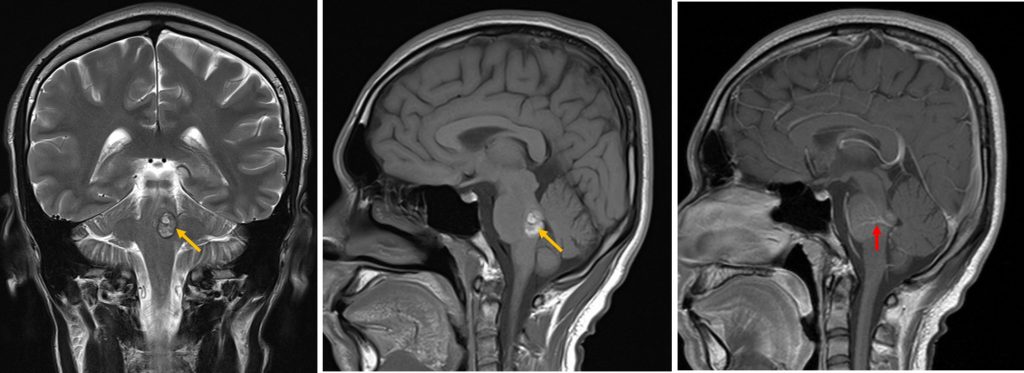
- A lobulated lesion in the left side of pons posteriorly which shows charateristic ‘popcorn’ appearance (yellow arrows).
- Variable T1 and T2 hyperintense with T2-hypointense rim is seen.
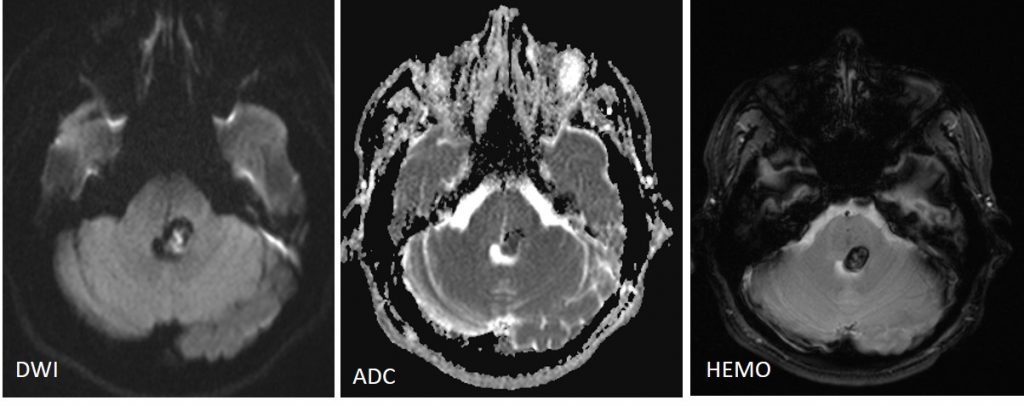
- Blooming also noted on Hemo sequence.
- A central area of restricted diffusion in keeping with late subacute bleed blood product.
- No enhancement post contrast, however a prominent veins are seen draining to ependymal surface of fourth ventricle (red arrows).
- Surrounding pons shows normal signal intensity
- No hydrocephalus. No abnormal leptomeningeal enhancement.
Diagnosis: Mixed vascular malformations (cavernoma and developmental venous anomaly)
Discussion:
- A mixed vascular malformation is a relatively common congenital cerebral vascular malformation
- Most frequently composed of a developmental venous anomaly (DVA) and a cavernous malformation
- As DVA seldom bleed, the risk of a mixed vascular malformation is determined by the other component
- DVA is also known as cerebral venous angioma = a congenital malformation of veins which drain normal brain. It is characterised by caput medusae sign of veins draining into a single larger containing vein which in turn either drains into a dural sinus or a deep ependymal vein. Usually an incidental finding seen in about 9% on contrast-enhanced MRI brain.
- Cavernous haemangiomas=cavernous malformation=cavernomas are common cerebral vascular malformations, third most common after DVA and capillary telangiectasia.