Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- A 44 years old lady
- Presented with right breast lump for 2 weeks duration.
- No fever, no pain, no nipple discharge
- No family history of breast cancer.
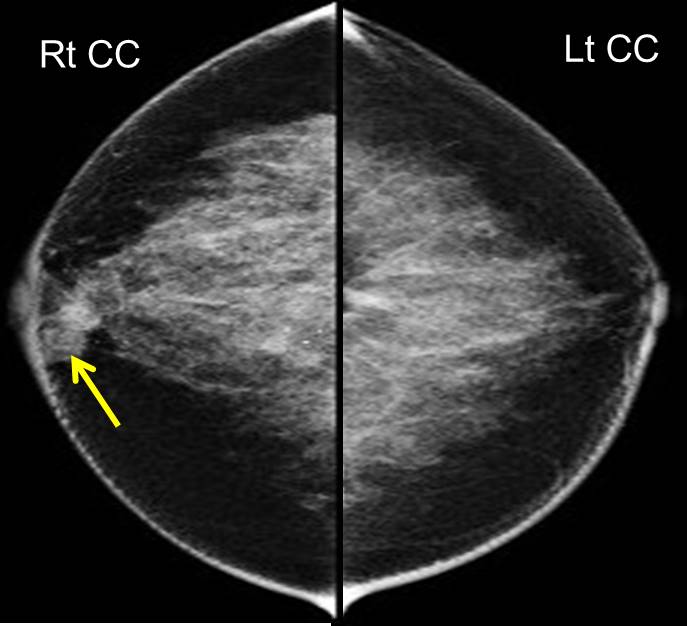
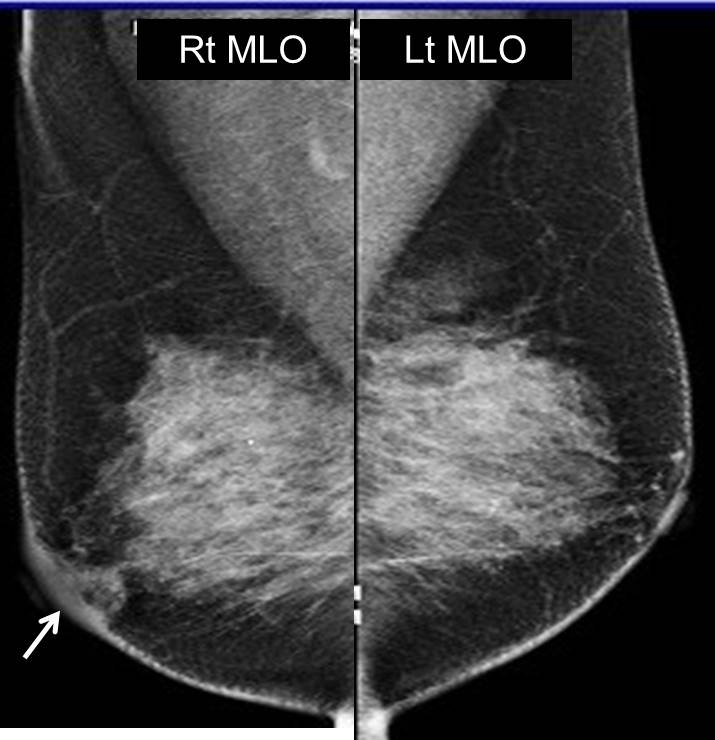
Mammogram findings:
- Bilaterally dense breasts with symmetrical parenchymal pattern
- An ill-defined low-density lesion is seen in the right retroareolar region (yellow arrow)
- Associated with focal skin thickening at periareolar
- No stromal distortion or suspicious clustered microcalcification
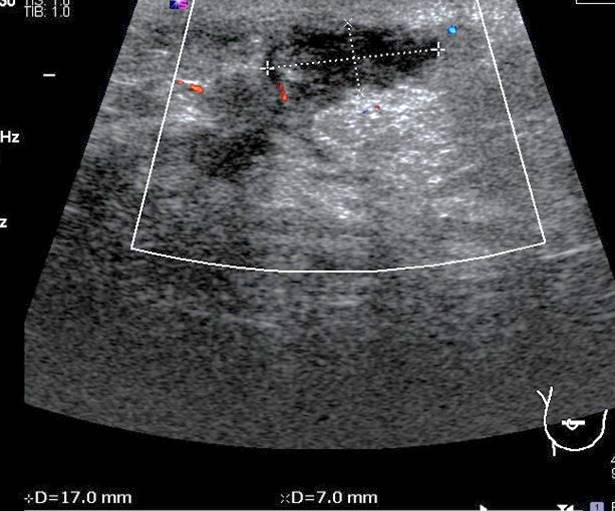
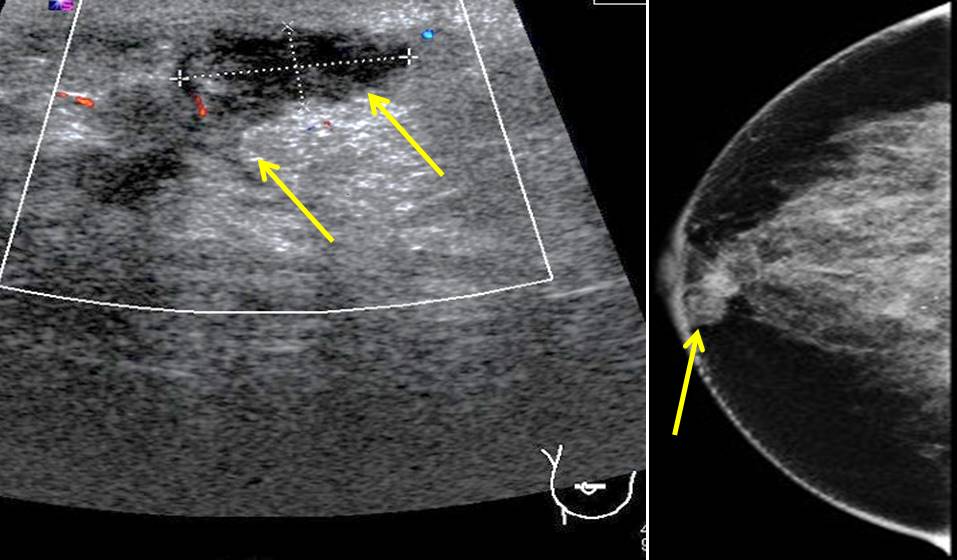
Ultrasound findings:
- An ill-defined hypoechoic lesion at right retroareaolar region
- The lesion is measuring 17 x 23 x 7 mm with increase in surrounding vascularity
- Internal echoes are seen within the lesion
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: biopsy specimen consists of a few strip of greyish tissue measuring 3-10 mm length
- Microscopy: section shows multiple pieces of breast tissue densely infiltrated by mixed acute and chronic inflammatory cells, predominantly neutrophils. There are presence of granulation tissue reaction with foci of multinucleated foreign body giant cells reaction and scattered foamy macrophages. Acute inflammatory exudates are noted in some of the pieces. No epithelioid granuloma or evidence of malignancy seen. PAS stain does not show any fungal bodies
- Interpretation: right retroareolar biopsy: acute on chronic mastitis
Diagnosis: Adult non-puerperal mastitis
Discussion:
- Non-puerperal mastitis is also known as non-lactating mastitis, encompasses all the causes of inflammatory changes in the female breast and mammilla not related to lactation.
- The aetiology of this disease is still unknown, but it may or may not be accompanied by infection
- The majority of patients with non-puerperal mastitis usually exhibit one or several breast masses without any other signs of inflammation
- It can be difficult to distinguish these symptoms from breast carcinoma and patients can easily be misdiagnosed as having an inflammatory breast carcinoma or an invasive carcinoma
- Mammographic findings are considered non-specific, and include focal asymmetric density (most common), non-circumscript lesions, masses or architectural distortion.
- Skin thickening in the mammary areola is more commonly observed in inflammatory breast carcinoma or invasive carcinoma.
- On ultrasound, the majority of the lesions were irregular, hypoechoic or mass-like lesions. Other ultrasound findings included lesions that were either separately or contiguously lamellar, tubular hypoechoic or non-mass-like.
Reference:
- H tan et al, Radiological and clinical features of adult non-puerperal mastitis. Br J Radiol 2013 Apr; 86 (1024): 20120657