Image 1:
Question 1: Name the examination.
Question 2: Name the labelled structures.
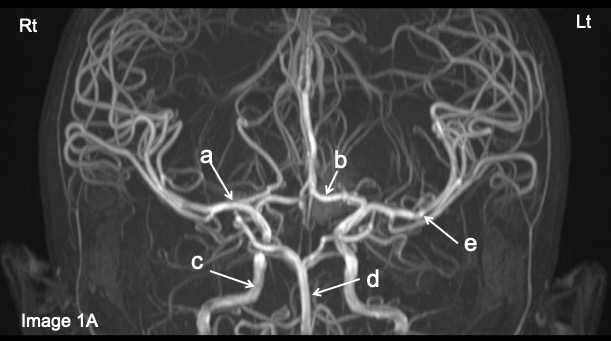
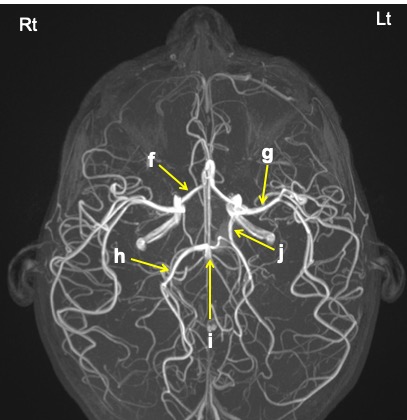
Image 2:
Question 1: Name the examination
Question 2: Name the labelled structures.
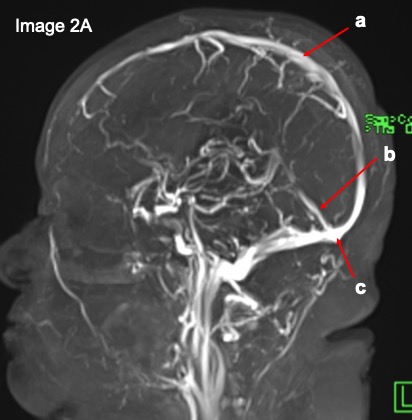
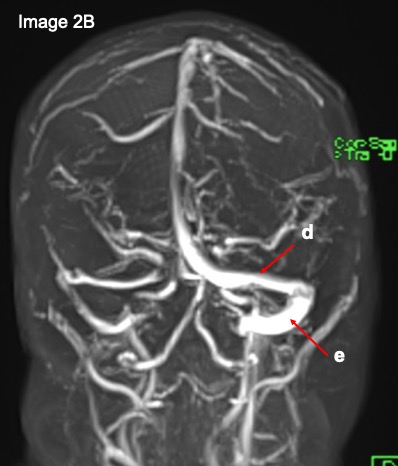
Image 3:
Question 1: Name the examination
Question 2: Name the labelled structures.
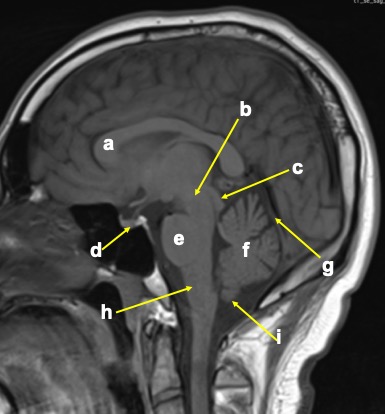
Image 4:
Question 1: Name the examination
Question 2: Name the labelled structures.
Question 3: Describe the course of structures ‘b’ and ‘e’
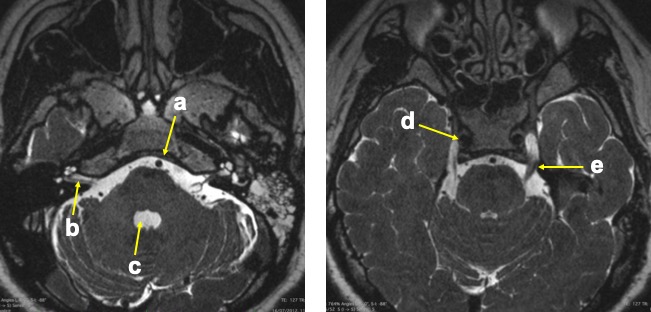
Image 5:
Question 1: Name the examination
Question 2: Name the labelled structures.
ANSWER:
Image 1:
Question 1: MR angiography MIP images
Question 2:
- a: Right middle cerebral artery
- b: Left anterior cerebral artery
- c: Right internal carotid artery
- d: Basilar artery
- e: Left middle cerebral artery
- f: Right anterior cerebral artery
- g: Left middle cerebral artery
- h: Right posterior cerebral artery
- i: Basilar artery
- j: Left posterior communicating artery
Image 2:
Question 1: MR venography
Question 2:
- a: superior sagittal sinus
- b: Straight sinus
- c: torcula herophili
- d: transverse sinus
- e: sigmoid sinus
Image 3:
Question 1: MRI brain in sagittal plane, T1-weighted image
Question 2:
- a: genu of corpus callosum
- b: midbrain
- c: quadrigeminal plate
- d: pituitary gland
- e: pons
- f: cerebellum
- g: tentorium cerebelli
- h: medulla oblongata
- i: tonsil of cerebellum
Image 4:
Question 1: MRI of cerebellopontine angle in T2-weighted images
Question 2:
- a: basilar artery
- b: right vestibulocochlear nerve
- c: fourth ventricle
- d: right internal carotid artery
- e: left trigeminal nerve
Question 3:
- b= vestibulocochlear nerve. The roots arise from the vestibular and cochlear nuclei located in the brainstem. The fibers from both roots merge to form the vestibulocochlear trunk of the nerve that is found in the posterior cranial fossa in the petrous part of the temporal bone. When the vestibulocochlear nerve reaches the inner ear, it again splits into the vestibular and cochlear part which supply target tissues of the inner ear.
- e= trigeminal nerve. The largest cranial nerves. It exits the brain by a large sensory root and a smaller motor root coming out of the pons at its junction with the middle cerebral peduncle. It passes laterally to join the gasserian (semilunar) ganglion in the Meckel cave.
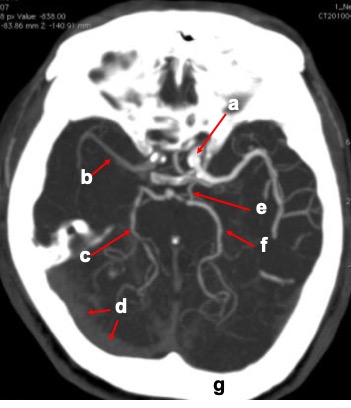
Image 5:
Question 1: CT angiography MIP image in axial plane.
Question 2:
- a: Left internal carotid artery
- b: Right middle cerebral artery
- c: Right posterior cerebral artery
- d: Right transverse sinus
- Left posterior communicating artery (PCOM)
- f: left posterior cerebral artery
- g: occipital bone
Recent Comments