Clinical:
- A 73 years old man
- Presented with chronic cough
- Associated with loss of appetite and loss of weight
Radiographic findings:
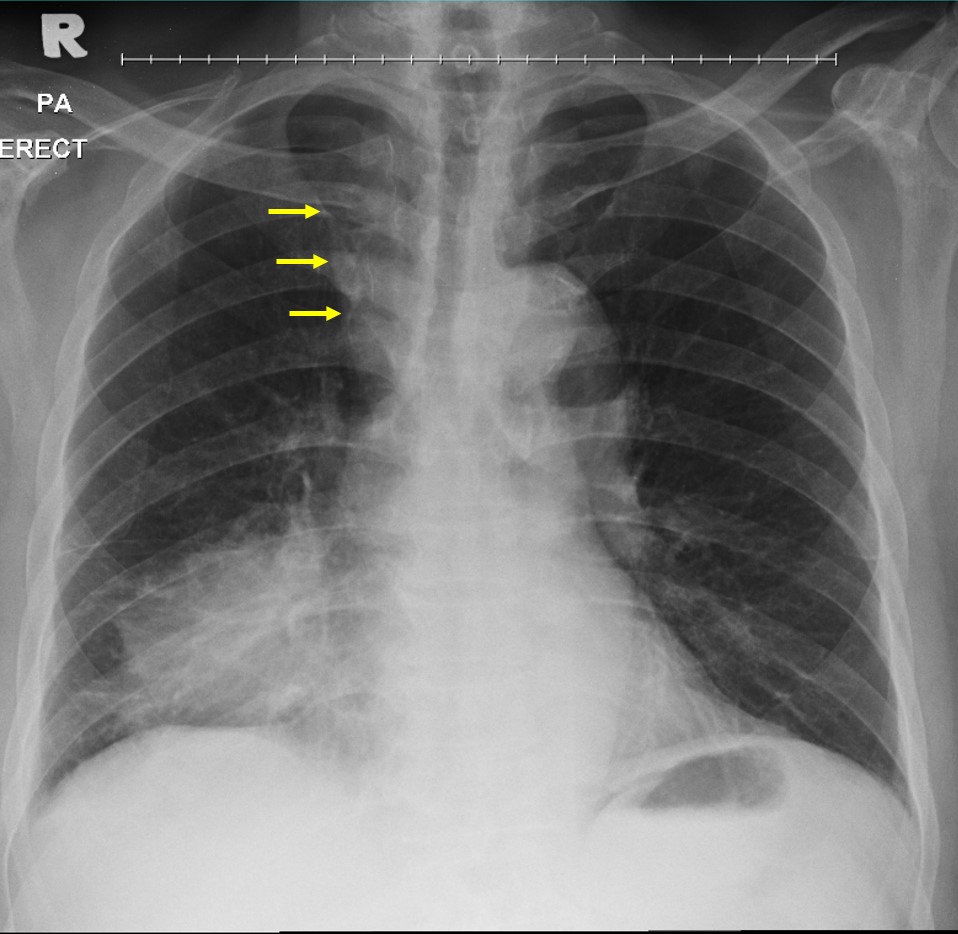
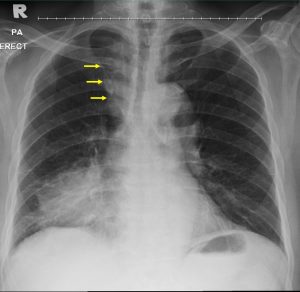
- There is opacity at lower zone of right lung.
- There is obliteration of right cardiac margin.
- The right hemidiaphragm is well visualized.
- There is widening of right superior mediastinum shadow (yellow arrows).
- No hilar mass. No cardiomegaly.
- No pleural effusion or pneumothorax.
- Bones are unremarkable.
CT findings:
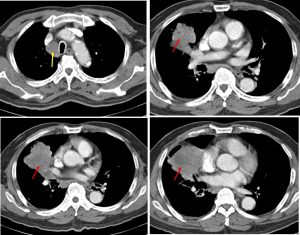
- There is a large mass in the right middle lobe measuring 66 mm. It showed heterogenous enhancement. No fluid levels or cavities within. No calcification within the lesion.
- Otherwise no other nodule or mass in both lungs.
- There is no pleural effusion. No pericardial effusion.
- Heart and great vessels are normal.
- There is slight compression causing luminal narrowing of distal trachea.
- There are multiple enlarged mediastinal nodes seen.
HPE findings:
- Macroscopy: specimen labelled as right middle lobe endobronchial lesion consist of few tiny whitish tissue measuring 4 mm in aggregate diameter.
- Microscopy: section shows multiple pieces comprising of necrotic tissue, cartilage and free floating malignant cellsas well as clusters of malignant cells infiltrating the desmoplastic stroma. These cells exhibit squamous differentiation as highlighted by positivity for p40 and negativity for TTF-1.
- Interpretation: squamous cell carcinoma
Diagnosis: squamous cell carcinoma of lung
Discussion:
- Squamous cell carcinoma represents 30% of all lung cancers
- It is the second most commonly seen lung cancer after adenocarcinoma
- In most cases are related to heavy smoking
- These tumours are more often centrally located within the lung and may grow much larger than 4 cm in diameter
- Cavitation is seen in up to 82%.
- They commonly cause segmental or lobar lung collapse due to their central location and relative frequency