Case1:
A 60 years old man with neck pain.
Question 1: Name the examination.
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
Question 3. Give diagnosis and possible differential diagnosis.
Question 4: What other radiological investigation can be done for this patient.
Case 2:
A 40 years old lady with headache. Had underlying hypertension and diabetes mellitus.
Question 1: Name the examination.
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
Question 3. Give diagnosis and possible differential diagnosis.
Question 4: What possible complication can occur in this case.
Case 3:
A 20 years old man with sudden onset of altered consciousness.
Question 1: Name the examination.
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
Question 3. Give your diagnosis.
Case 4:
Question 1: Name the examination.
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
Question 3. Give diagnosis and possible differential diagnosis.
Question 4: What other radiological investigation can be done for this patient.
Case 5:
Question 1: Name the examination.
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
Question 3. Give diagnosis and possible differential diagnosis.
ANSWERS:
Case 1:
Question 1: Name the examination.
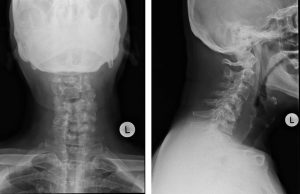
Radiograph of cervical spine in AP and lateral views
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
- Loss of normal cervical lordosis.
- Reduction in heights of C5 and C6 vertebral bodies
- Sclerotic change of the residual visualized C5 and C6 vertebrae
- The C4/C5 and C5/C6 intervertebral spaces are not seen.
- On AP view, the pedicles of the involved C4, C5, and C6 vertebra are also not visualized.
- The C4 vertebra body appears partly sclerosed. However its height is still preserved.
- There is prevertebral soft tissue swelling from C3/C4 intervertebral disc level until the T1 vertebral body level. This swelling is centered predominantly at the level of the destroyed cervical vertebral bodies. The thickest area measures about 2.7 cm.
- The rest of the visualised bones are normal.
Question 3. Give diagnosis and possible differential diagnosis.
Diagnosis: Tuberculous spondylitis, differential diagnosis: metastatic compression fracture, osteoporotic compression fracture, trauma
Question 4: What other radiological investigation can be done for this patient.
Other radiological investigations include CT scan of the cervical spine or MRI of the cervical spine.
For further reading on this case, you can visit http://radiologycases.my/2020/07/07/tuberculous-spondylitis-2/
Case 2:
Question 1: Name the examination.
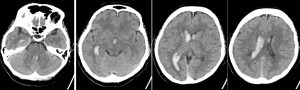
CT scan of the brain in axial plane, soft tissue window non-contrasted study.
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
- Hyperdensities are seen in the lateral ventricles (more on the right side), third ventricle and also fourth ventricle.
- There is associated minimal dilatation of the ventricles
- No midline shift and no mass effect
- No internal brain herniation
Question 3. Give diagnosis and possible differential diagnosis.
Intraventricular hemorrhage possible due to trauma, hypertension or ruptured aneurysm
Question 4: What possible complication can occur in this case.
Hydrocephalus and internal brain herniation.
Case 3:
Question 1: Name the examination.
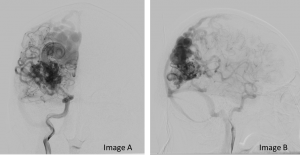
Digital subtraction cerebral angiography in frontal (Image A) and lateral (Image B) projection.
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
- There are large serpenginous dilatations of vessels seen
- It is located in the right parieto-occipital region.
- The arterial supply and the draining veins are seen.
Question 3. Give your diagnosis.
Brain arteriovenous malformations
To read more about this case, you can visit http://radiologycases.my/2020/07/07/cerebral-arteriovenous-malformations
Case 4:
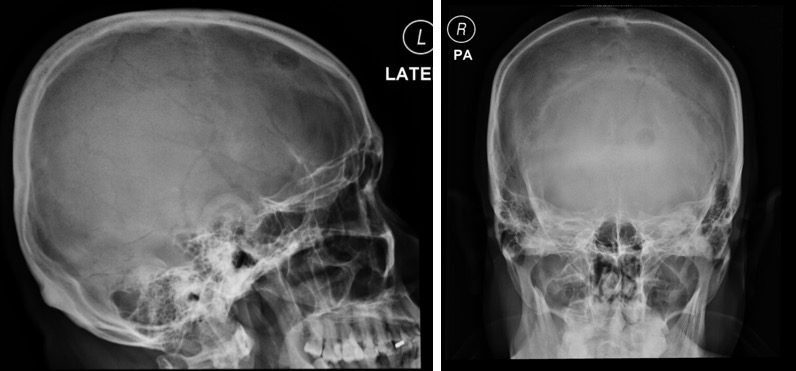
Question 1: Name the examination.
Skull radiograph in lateral and frontal projections.
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
- A rounded lytic lesion is seen at left frontal bone.
- Its outline is well delineated. No sclerotic border.
- No fluid fluid level. No internal matrix.
- No other lesion elsewhere.
- No obvious soft tissue swelling.
Question 3. Give diagnosis and possible differential diagnosis.
Metastasis, multiple myeloma, osteomyelitis, brown’s tumour, eosinophilic granuloma
Question 4: What other radiological investigation can be done for this patient.
CT scan of the brain or MRI of brain
For further reading on this case, you can visit http://radiologycases.my/2020/07/06/lytic-skull-metastasis
Case 5:
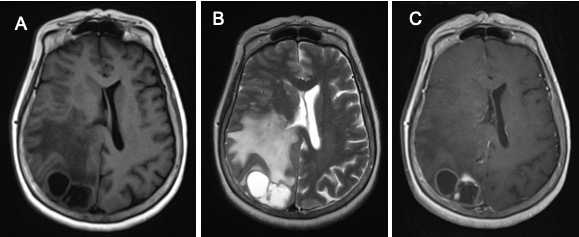
Question 1: Name the examination.
MRI of the brain in axial planes, T1-weighted image (A), T2-weighted image (B) and T1+post contrast (C)
Question 2: Describe the abnormality seen.
- There are multiple rounded lesions in the right occipital lobe
- The lesions are hypointense on T1WI and hyperintense on T2WI
- It shows ring-enhancement on post contrast image
- The lesion has thin wall, irregularity of the wall is seen in one of the lesion
- Mass effect with compression of the right lateral ventricle
- No midline shift, no hydrocephalus
Question 3. Give diagnosis and possible differential diagnosis.
Multiple ring-enhancing lesions: causes include cerebral abscess, cerebral metastasis, tuberculomas or primary brain tumours.
Thank you