Case contribution: Dr Radhiana Hassan
Clinical:
- An 11 year old female
- Trauma, electric scooter vs electric scooter
- Complaint of pain and swelling over right knee
- Unable to weight bear and unable to fully extend right knee
- Clinical examination shows swollen right knee with limited ROM 30-90 degrees, generalized tenderness around knee region
- Sensation intact, no foot drop
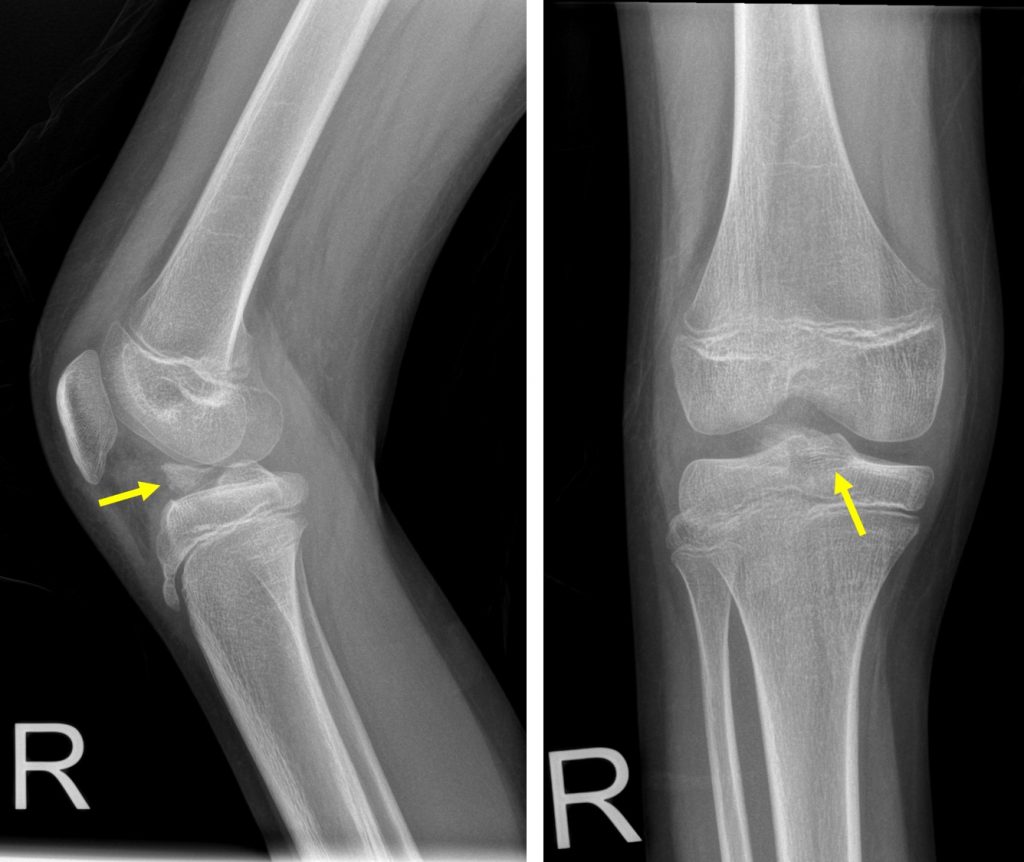
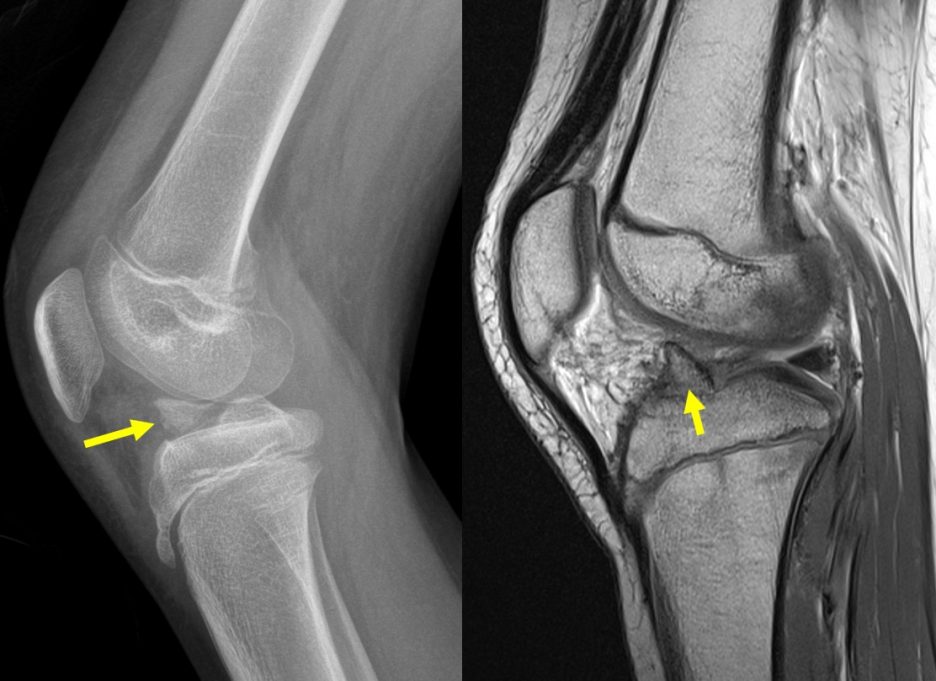
Radiograph of right knee in AP and lateral views:
- bone fragment seen within the joint space
- Associated irregularity seen at base of tibial eminence
- No other fracture seen
- No obvious soft tissue swelling
- No radiopaque foreign body
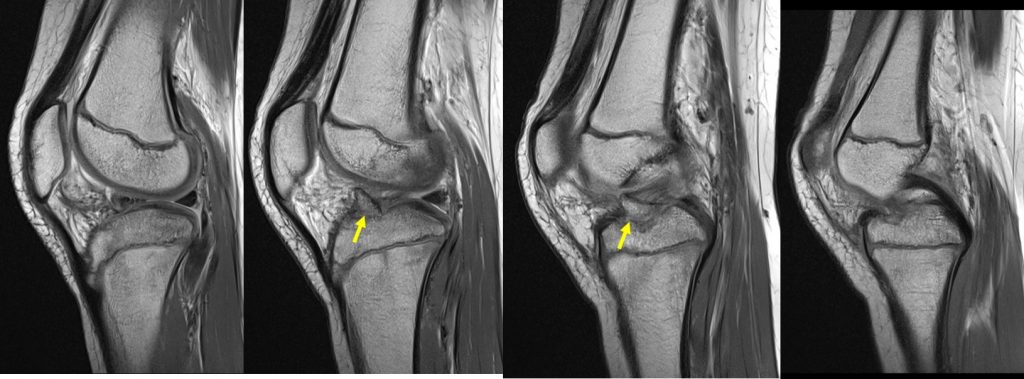
MRI of right knee:
- Sagittal T2-weighted images show the avulsion fracture (yellow arrows)
- The avulsion fracture of tibial eminence is seen at the anterior intercondylar notch, at the attachment site of the ACL.
- There is buckling of ACL with some heterogeneous signal and fluid seen at the anteromedial bundle.
- However the continuity of the ligament is preserved.
- There is also positive Blumeensaat angle.
- The posterior cruciate ligament (PCL) is intact and normal.
- No apparent PCL buckling is seen.
Intra-operative findings:
- Avulsed fracture at base of tibial eminence
- ACL substance intact
- Fibrous tissue surrounding the fracture fragment removed
- Medial and lateral meniscus intact
- Arthroscopic and pull through suture right tibial eminence done
Diagnosis: Avulsion fracture of ACL (anterior cruciate ligament)
Discussion:
- ACL avulsion fracture or tibial eminence avulsion fracture
- It is seen as separation of the tibial attachment of the ACL to variable degrees’
- Separation at femoral attachment is rare
- It is more common in children than adult
- There may be anterior translation of the femur on the tibia on lateral views
- Classification (Meyers and McKeevers system)
- Type 1: minimally/non-displaced fragment
- Type 2: anterior elevation of the fragment
- Type 3: complete separation of the fragment
- 3a-involves small portion of the eminence
- 3b-involves the majority of the eminence
- Type 4: comminuted avulsion or rotation of the fracture fragment